Corporate social responsibility measurement has evolved from feel-good stories to rigorous data analysis. Companies now track social impact with the same precision they apply to financial performance, creating accountability systems that drive genuine community development.
Organizations across the Philippines are adopting sophisticated measurement frameworks that demonstrate both social outcomes and business value, responding to growing demands from investors and stakeholders for proof of lasting change.
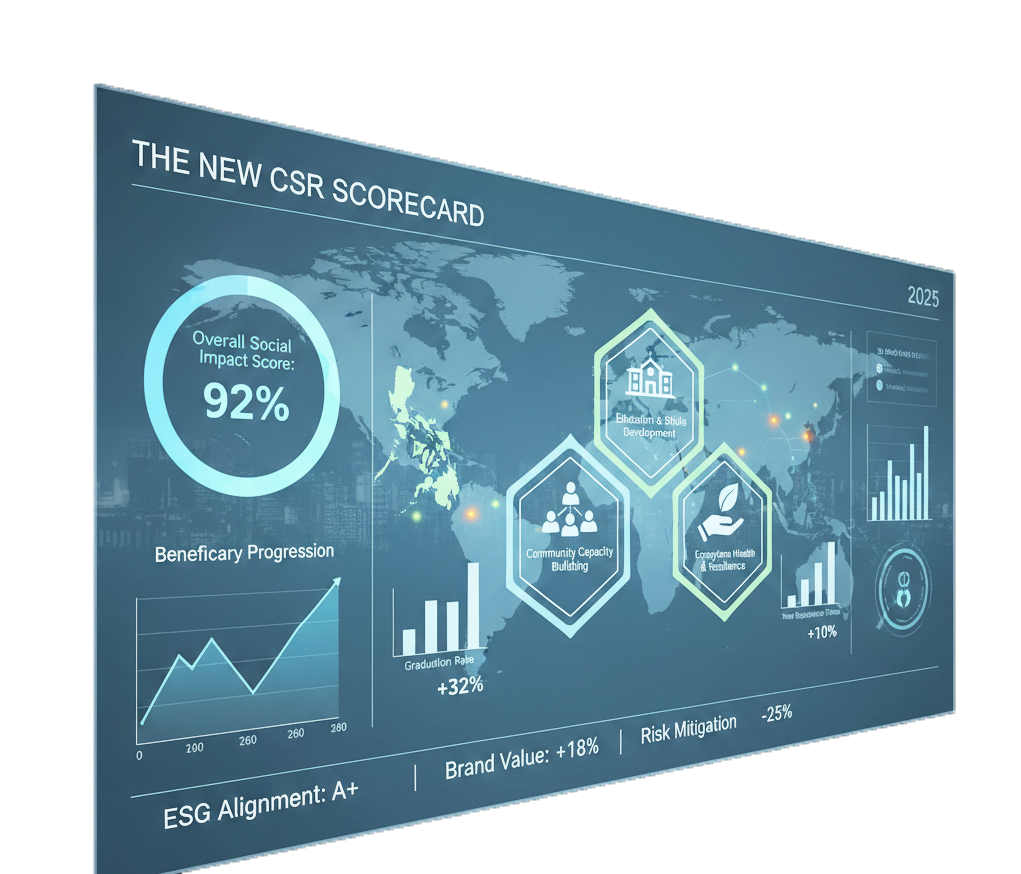
Beyond traditional metrics
Traditional CSR reporting focused on inputs—money donated, volunteers deployed, events organized. Modern frameworks measure outcomes and long-term impact. Companies now track beneficiary progression, community capacity building, and systemic changes that extend beyond program duration.
Educational programs measure graduation rates, employment outcomes, and career advancement over multiple years rather than just scholarship recipients. Livelihood initiatives track income increases and business sustainability. Environmental programs monitor ecosystem health and community resilience.
This approach requires companies to invest in tracking systems that follow beneficiaries for years, measuring how interventions create lasting changes in individual lives and community conditions.
The transparency – trust connection
Recognition programs like the 3G Excellence in Sustainability Reporting Award highlight companies that demonstrate transparency in their sustainability disclosures. Winners showcase comprehensive reporting with verified data and clear impact attribution.
Award-winning reports integrate financial and social metrics, showing how CSR investments generate returns through brand enhancement, risk mitigation, and operational efficiency. They include third-party verification and honest assessments of program limitations alongside successes.
When companies commit to public reporting with specific metrics and timelines, they create internal pressure for program effectiveness that drives continuous improvement.
Data-driven design
Modern CSR programs begin with baseline assessments and models that predict how interventions will create desired outcomes. Companies establish key performance indicators before program launch, enabling real-time monitoring and course corrections.
Technology platforms support data collection through mobile applications and digital surveys. Beneficiaries provide feedback directly through digital channels, while community partners upload progress reports documenting program implementation.
Analytics capabilities allow companies to identify which program components generate the strongest impact, optimize resource allocation, and scale successful interventions while discontinuing ineffective approaches.
Multiple perspectives matter
Effective measurement systems incorporate stakeholder perspectives rather than relying solely on corporate-defined metrics. Community members, government partners, and civil society organizations contribute to indicator development and impact assessment.
Communities establish their own monitoring systems while companies provide technical support. This approach ensures programs address genuine priorities rather than imposed solutions. Regular stakeholder consultations inform program adjustments and expansion strategies.
Financial integration and ROI
CSR measurement increasingly integrates with financial reporting, demonstrating how social investments create business value. Companies track direct cost savings from environmental programs, employee engagement improvements, and brand value enhancement from social impact.
Return on investment calculations include operational efficiency gains, risk mitigation value, and talent attraction benefits. Some organizations adopt social return on investment methodologies that quantify social benefits in monetary terms, enabling direct comparison between social and financial returns.
Technology-aided tracking
Digital platforms enable real-time data collection, automated analysis, and dynamic reporting. Mobile applications allow field staff to upload photos, conduct surveys, and track beneficiary progress from remote locations.
Blockchain technology creates tamper-proof records of social impact data, enhancing credibility between organizations. Artificial intelligence analyzes datasets to identify patterns, predict outcomes, and recommend program improvements.
Industry standardization
Organizations like the Global Reporting Initiative and UN Global Compact provide guidance for consistent impact measurement. Standardization helps investors evaluate CSR performance across portfolios while enabling companies to benchmark progress against industry peers.
However, programs addressing local community needs require customized indicators that reflect unique challenges while maintaining comparability on core outcome areas.
Long-term community impact
Sophisticated measurement systems track community-level changes beyond individual program beneficiaries. Companies monitor local economic development, social cohesion, and institutional capacity over multi-year periods.
Effective programs should strengthen community capacity for self-directed development rather than creating dependency. Longitudinal studies follow communities for 5-10 years after program completion, measuring sustained benefits and identifying factors that contribute to lasting impact.
ESG alignment
Leading companies integrate CSR metrics into sustainability reports that align with Environmental, Social, and Governance investment criteria. These reports demonstrate how social impact contributes to overall company performance and long-term value creation.
ESG alignment ensures CSR measurement addresses investor concerns about sustainability risks and opportunities. Companies show how community development programs build social license to operate while environmental initiatives reduce operational risks.
Building credible systems
Credible impact measurement requires independence, rigor, and transparency. Companies increasingly engage third-party evaluators to assess program effectiveness and verify reported outcomes.
Measurement systems must balance comprehensiveness with practicality. Effective frameworks focus on key indicators that drive decision-making rather than overwhelming program staff with complex tracking requirements.
The evolution toward rigorous impact measurement reflects CSR’s maturation from charitable activity to strategic investment. Companies that master these approaches demonstrate genuine social impact while building competitive advantages through community development partnerships.
Organizations demonstrate how sophisticated measurement systems create accountability, drive program effectiveness, and build stakeholder confidence in corporate social responsibility initiatives.





